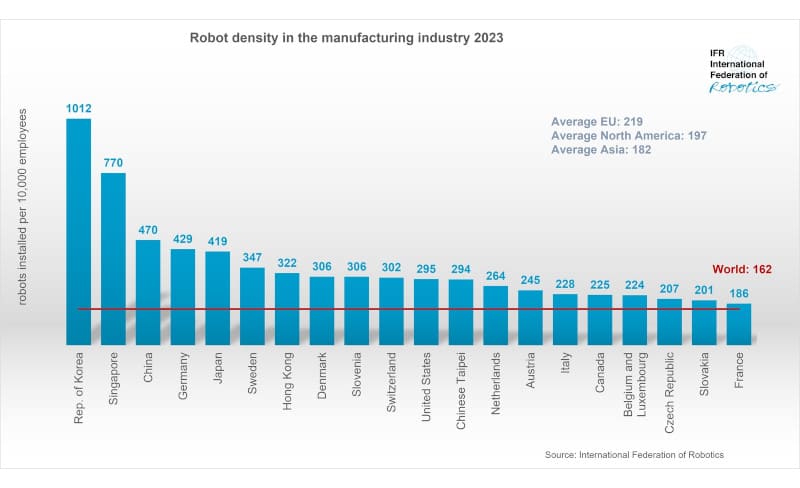
The adoption of robots in factories around the world is progressing rapidly, with the new global average robot density reaching a record figure of 162 robots per 10,000 employees in 2023, more than double the figure seven years ago (74 robots). This was revealed by the World Robotics 2024 report published by the International Federation of Robotics (IFR).
“Robot density serves as a barometer to measure the level of automation in manufacturing around the world,” said Takayuki Ito, president of the International Federation of Robotics. “China comes in second this year, third in the world after South Korea and Singapore, but tied with Germany and Japan.”
Robot density by region
The European Union has a robot density of 219 robots per 10,000 employees, an increase of 5.2%, with Germany, Sweden, Denmark and Slovenia in the top 10 in the world.
In North America, robot density is 197 robots per 10,000 workers, up 4.2%. The United States is one of the 10 most automated countries in manufacturing.
Asia’s robot density is 182 robots per 10,000 manufacturing employees, an increase of 7.6%. The economies of South Korea, Singapore, mainland China and Japan are among the 10 most automated countries.
Top Countries
South Korea is the world’s largest user of industrial robots, with 1,012 robots per 10,000 employees. Since 2018, robot density has increased by an average of 5% each year. With a world-renowned electronics industry and a strong automotive industry, the Korean economy relies on two of the largest buyers of industrial robots.
Singapore follows with 770 robots per 10,000 employees. Singapore is a small country.
Manufacturing has a very small number of employees, so a high robot density can be achieved even with a relatively small number of factories.
China will overtake Germany and Japan in 2023 to take third place. The country’s increased use of automation technologies has led to a high robot density of 470 robots per 10,000 employees (2022: 402). China only entered the top 10 in 2019. It managed to double its robot density in four years.
Germany is in fourth place with 429 robots per 10,000 employees. Robot density in Europe’s largest economy has increased by an average of 5% per year since 2018.
Japan is in fifth place with 419 robots. Robot density in the world’s leading robot-producing countries increased by an average of 7% annually (2018-2023).
Robot density in the United States will reach 295 robots in 2023. This will rank the country 10th in the world.