Collaborative robots (cobots), an emerging category of robots, have gained significant momentum over the past decade. Unlike traditional industrial robots that need physical fences, collaborative robots can work side by side with human operators without physical separation, thereby taking less space. As a result, collaborative robots, also known as cobots, are ideal options for small and medium enterprises (SMEs) thanks to their low costs, small footprint, ease of use, flexibility, and low power consumption. As large companies aim to bring human workers back to manufacturing, cobots are expected to be increasingly adopted over the next two decades.
Cobots can be used for various tasks, including packaging, palletizing, machine tending, and quality inspection across multiple industries such as automotive manufacturing, food and beverage, electronics, hospitality and healthcare. IDTechEx’s latest report ‘Collaborative Robots (Cobots) 2023-2043: Technologies, Players and Markets’ takes a deep dive into the applications and tasks mentioned above with an in-depth analysis of the key enabling technologies, players and markets with granular forecasts for the next 20 years.
Collaborative robots in automotive manufacturing
As the most prominent application, cobots are used for a few tasks, including car assembly, and surface polishing. With the increasing popularity of electric vehicles, many existing car production lines need retrofitting or reconstruction. One of the pain points of large automakers is that if one industrial robot malfunctions, the entire production line must be closed to ensure the safety of human operators during the inspection. This process could lead to a significant downtime cost. However, cobots can be an ideal solution as human operators can work closely with them without affecting other robots.

Meanwhile, large automotive manufacturers (e.g. Audi, Volkswagen, etc.) have proposed ‘intelligent factories’ where they aim to enhance the flexibility of their production by improving human-robot interaction. Thanks to their flexibility, IDTechEx predicts that cobots in the car manufacturing industry will have an average CAGR of 27.2% for the upcoming two decades.
Collaborative robots in the food and beverage industry
The modern food industry is transitioning to high mix low volume (HMLV) production that requires increasing production flexibility. HMLV manufacturing, also known as make-to-order manufacturing, is the process of producing a high variety of products in small quantities. The rising mix of food products also leads to a soaring demand for packaging. At this stage in 2022, most packaging is still done manually.
However, due to COVID, border closures, and labor shortages, many food product suppliers have started to consider automating their food packaging process by adopting collaborative robots. As packaging requires robots with a low payload and high flexibility, it can be an ideal use case for cobots. Although the food and beverage industry has historically not been the primary target industry for cobots, IDTechEx has observed that more cobot makers are starting to use a long-tail strategy and make increasing efforts in the food and beverage industry for the next 20 years.
The IDTechEx report addresses the applications above with analysis including several case studies, along with concerns from SMEs owners and solutions to these concerns.
Collaborative robots in the electronics industry
The electronics industry is an emerging application for collaborative robots. The main task of cobots is electronics quality inspection, including phone chip inspection, PCB inspection, and PC processor inspection. Although it is believed that the annual shipment of smartphones and PCs will remain stable or decrease slightly in the next two decades, IDTechEx believes that the global demand for PCBs will continue to rise because of the increasing demand for other electronics. Furthermore, compared with manual inspection, using cobots for electronics inspection could significantly increase efficiency and accuracy and minimize potential human errors. Nevertheless, despite the growth, IDTechEx believes that the increase of cobot adoption in this industry will not be as fast as in the application areas mentioned above..

Collaborative robots in the healthcare and hospitality industry
The healthcare and hospitality industry is an emerging area for collaborative robots. A subsector within this area is cobots in surgical applications, where surgeons remotely control cobots to perform surgery. In addition, mobile cobots can also be widely used in care homes to support health workers.
As an emerging application, IDTechEx has noticed an increasing investment in this area, and IDTechEx’s report includes use cases, along with challenges and solutions.
Emerging technologies – sensors
Sensors are one of the most important enabling technologies for collaborative robots. The most typical sensors used in cobots for safety are torque sensors, where a range of sensor values are pre-set, and if a collision occurs, the values will exceed the range, which triggers the robot’s emergency stop. However, IDTechEx has noticed a number of emerging sensors (e.g. tactile, proximity, etc.) to provide safety, but they have not been widely adopted in the market so far.
The IDTechEx report addresses these sensory technologies with a detailed analysis of torque sensors, capacitive sensors, and proximity detection sensors.
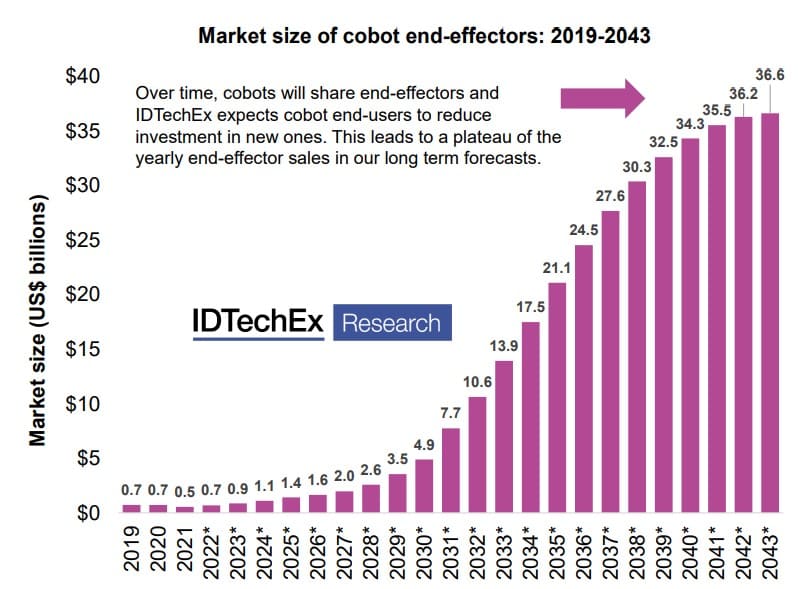
Emerging technologies – end-effectors
End-effectors, also known as end-of-the-arm-tooling, are designed to enable robots to interact with their tasks. End-effectors can be classified as mechanical or electromechanical components depending on actuation principles. Typical end-effectors include grippers, process tools, and sensors.
IDTechEx believes that the end-effector market will increase with the increasing adoption of cobots. However, since different cobots can share end-effectors, the end-effector market is predicted to saturate earlier than the cobot market.

